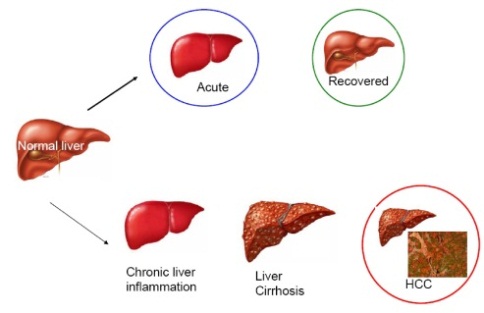
Difference Between Acute and Chronic Hepatitis B:
Hepatitis B is a serious disease that can lead to liver scarring, liver failure, or liver cancer. Most people who contract hepatitis B in adulthood recover completely, even if the symptoms are severe and intense. In contrast, children and infants are usually more prone to developing chronic and persistent infections.
- Acute Hepatitis B:
When infected with hepatitis B, 95% of adults will clear the virus from their body within a few months due to their immune system. After recovery, individuals will not contract the virus again because they develop antibodies against it, which can be detected through the Anti-HBs blood test. A positive Anti-HBs test means that the patient has recovered from the disease and will not become reinfected. They are also not a carrier of the virus and cannot transmit it to others. This test will also be positive after receiving the hepatitis B vaccination.
- Chronic Hepatitis B:
Chronic hepatitis B occurs in about 5% of adults, 25% to 50% of children under the age of five, and 90% of newborns infected with the virus. In these cases, the immune system cannot clear the virus, leading to chronic infection or being a carrier of the virus. This makes them susceptible to complications of chronic hepatitis and poses a risk of transmitting the infection to others.
From the book “100 Questions About the Liver” by Professor Dr. Gamal Shiha, Chairman of the Board of Trustees of the Egyptian Liver Foundation and Chairman of the Education and Scientific Research Committee in the House of Representatives.